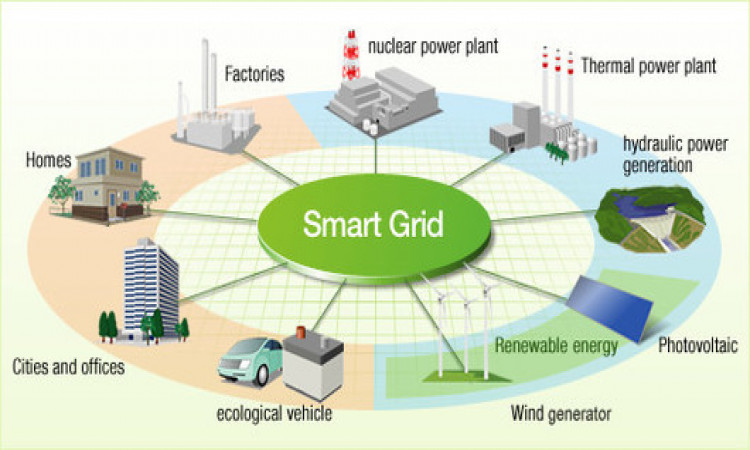
The introduction of smart grids has caused a fundamental re-engineering of the electricity service industry. Smart grid solutions are electricity networks that are founded on digital technology, which is utilized for delivering electricity to consumers by means of two-way digital communication. The entire smart grid system is automated for monitoring electricity usage at all locations. This system allows monitoring, control, and communication & analysis within the supply chain for assisting with curbing energy use & expenses, improving efficiency & maximizing reliability & transparency of the energy supply chain. Therefore, the need for future electrical systems or smart grid solutions can be traced to four drivers that are:
• Efficiency: Smart grids improve the efficiency of power generation & decrease the losses in consumption, transmission & distribution of electrical energy.
• Reliability: This implies delivering quality electrical energy whenever needed.
• Capacity: This implies fulfilling the increasing worldwide demand for electrical energy.
• Sustainability: This has to do with ensuring the effective incorporation of renewable power generation.
The smart grid solution was brought in with the objective to overcome the shortcomings of traditional electrical grids by utilizing smart net meters. Many government institutions worldwide have been encouraging the utilization of smart grid solution for their latent ability to control & cope with global warming, energy independence scenarios & emergency resilience. The smart grid solutions are equally beneficial for retail stores, hospitals, enterprises, multinational corporations & universities.
Features & Benefits of Smart Grids
The Smart Grids are associated with many features & benefits, which include
Demand response support: This provides users with an automated way of decreasing their electricity bills by directing them on how to utilize the low-priority electronic devices when the prices are lower.
Load handling: The total load of the power grid cannot be steady as it keeps changing over time. Thus, in situations of heavy load, a smart grid solution can counsel consumers to temporarily reduce energy consumption.
Decentralization of power generation: A distributed or decentralized grid system allows individual users to produce onsite power by utilizing any suitable method available.
Quicker reinstatement of electricity post power disturbances: Smart grid provides more efficient electricity transmission & increased incorporation of the large-scale renewable energy systems are all benefits.
Reduced management & operations expenses for utilities & lower power expenses for consumers, decreased peak demand that’ll assist with reducing electricity rates & better incorporation of customer-owned power generation systems are also some noted benefits of the smart grid.
Smart Grids can spot power theft & equipment failures: Certain “smart grid” networks come with dual functions. This incorporates advanced metering infrastructure systems; this system, when combined with different software, can be utilized for recognizing power theft &, by way of elimination, identify where equipment failures have occurred. These are in addition to its key function of measuring the time-of-use of electricity & doing away with the requirement for a human meter reading.
Moreover, a smarter grid would contribute resiliency to your electrical power system & will ensure that it is better prepared for tackling emergencies such as earthquakes, severe storms, terrorist attacks & huge solar flares. Owing to the two-way interactive ability of smart grid solutions, the smart grid would enable automatic rerouting whenever there are outages or equipment failures. This will help to lessen the outages & limit the effects when they do occur. Should there be a power outage, the smart grid technologies would identify & isolate the outages, restraining them before they take the shape of large-scale blackouts. Thus the new technologies will also assist with ensuring that electricity recovery starts quickly & strategically following an emergency- routing electricity quickly. Furthermore, the smart grids would take better advantage of the customer-owned power generators for creating power when it is not available from utilities.
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. required fields are marked *






{{comments.length}} Comments
{{ comment.name }}
{{comment.datetime}} Reply{{comment.message}}
{{ comment.name }}
{{comment.datetime}}{{comment.message}}